This topic describes working with methods that influence the text position.
Using default text position
To use the default text position for the current set of parameters, use the useDefaultTextPosition() method, which requires no parameters and sets the text position to the default value.
For example:
pDimension->useDefaultTextPosition();
To allow users to set a specific position for text, use the useSetTextPosition() method.
For example:
pDimension->useSetTextPosition();
Text position
To get the position of the dimension text, use the textPosition() method, which requires no parameters and returns the text position as an OdGePoint3d object.
For example:
OdGePoint3d textPos = pDimension->textPosition();
odPrintConsoleString(L"\nText position is %f %f %f", textPos.x, textPos.y, textPos.z);
To set a new position for dimension text, use the setTextPosition() method, which requires one OdGePoint3d parameter to specify the new position.
For example:
pDimension->setTextPosition(OdGePoint3d(3.0,4.0,0.0));
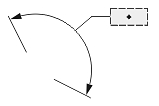
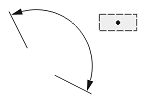
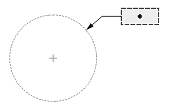
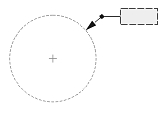
Interpretation of the text position depends on the Dimtmove value and type of dimension.
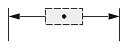
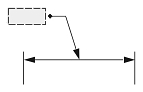
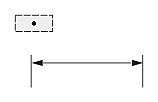
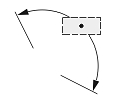
| Text Position | ||
| The center of the text box with the dimension line | The start point of the leader line, or the center of the dimension text box, or the start point of the dimension line | The center of the text box independent of the dimension line |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
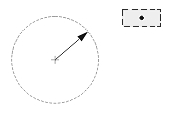 |
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Dimtmove value | ||
If Dimtmove is set to 0, the center of the dimension text box defines the text position. Then, if you change the text position, the dimension line moves together with the dimension text box.
If Dimtmove is set to 1, the text position depends on the dimension type. The text position is the start point of the leader line for aligned and rotated linear dimension entities; the center of the dimension text box for angular, ordinate, radial large, and arc-length dimension entities; and the start point of the dimension line for diametric and radial dimension entities. If the dimension text box is moved, the dimension entity automatically calculates the text position and adds the leader line.
If Dimtmove is set to 2, the center of the dimension text box defines the text position value. Then, the dimension text box and dimension lines can be placed anywhere independent of one another without a leader.
Note: For setting the text position you should call the useSetTextPosition() method first.
Text rotation
To get the text rotation angle, use the textRotation() method, which returns the angle as a double value.
For example:
odPrintConsoleString(L"\nText rotation is %f",pDimension->textRotation());
To set the new text rotation angle, use the setTextRotation() method, which requires one double parameter to specify the new angle.
For example:
pDimension1->setTextRotation(1);
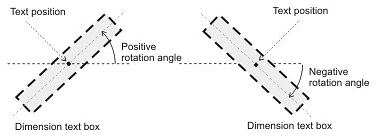
A positive value rotates the dimension text box counterclockwise (to the left). A negative angle rotates the dimension text box clockwise (to the right). The initial value is 0.0.
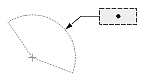
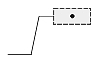
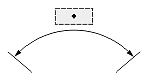
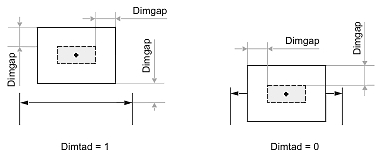
Dimtad
The Dimtad value indicates the vertical justification for the dimension text box relative to the dimension line. The vertical justification is an integer value and can be one of the following:
- 0 — The dimension text is centered vertically between two parts of the dimension line. This is the initial value.
- 1 — The dimension text is placed above the dimension line, except when the dimension line is not horizontal and the dimension text box is aligned horizontally.
- 2 — The dimension text box is placed on the side of the dimension line farthest from the defining point.
- 3 — The dimension text is positioned according to Japanese Industrial Standards.
- 4 — The dimension text is placed under the dimension line.
| Linear dimension | Angular dimension | Radial dimension | Ordinate dimension | |
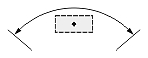
| Dimtad = 0 |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Dimtad = 1, Dimtad = 2 | 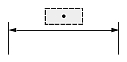 |
 |
 |
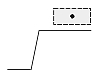 |
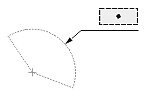
| Dimtad = 4 | 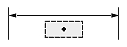 |
 |
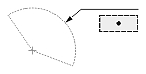 |
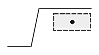 |
To get the Dimtad value, use the dimtad() method, which returns the Dimtad value as an OdInt16 value.
For example:
odPrintConsoleString(L"\nDimtad value = %d", pDimension->dimtad());
To set a new Dimtad value, use the setDimtad() method, which requires one OdInt16 parameter as a new Dimtad value.
For example:
pDimension->setDimtad(4);
Dimtvp
The Dimtvp value specifies, as a factor of DIMTXT, the vertical distance of the middle of the dimension text with respect to the dimension line.
To get the Dimtvp value, use the dimtvp() method, which returns the Dimtvp as a double value.
For example:
odPrintConsoleString(L"\nDimtvp value is %f", pDimension->dimtvp());
To set a new Dimtvp value, use the setDimtvp() method, which requires one double parameter as a new Dimtvp value.
For example:
pDimension->setDimtvp(1.5);
Dimgap
The Dimgap value specifies the distance between the dimension text box and the dimension, extension, or leader line according to the text position and text movement.
If Dimtad is set to 1 or 2, the Dimgap value specifies the distance from the bottom margin of the dimension text box to the dimension, extension, or leader line. If Dimtad is set to 0, the Dimgap value specifies the distance from the left and right margins of the dimension text box to both parts of the dimension line or the distance from the left margin of the dimension text box to the extension or leader line.
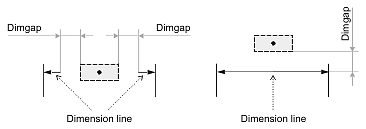
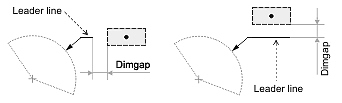
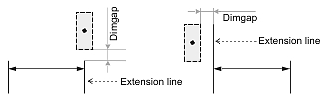
If the Dimgap value is negative, the dimension entity draws the border around the dimension text box:
If the Dimgap value is zero, the dimension entity attaches the dimension text box to the dimension, extension, or leader line.
The initial value is 0.
To get the Dimgap value, use the dimgap() method, which returns Dimgap as a double value.
For example:
odPrintConsoleString(L"\nDimgap value is %f", pDimension->dimgap());
To set a new Dimgap value to a dimension entity, use the setDimgap() method, which requires one double parameter as a new Dimgap value.
For example:
pDimension->setDimgap(0.2);
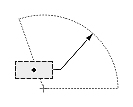
Dimtih
The Dimtih value is responsible for how the dimension text box is aligned inside the extension lines or definition entity for all dimension types except ordinate.
If the Dimtih value is true, the dimension text box is horizontally aligned when it is placed inside the extension lines or definition entity.
If the Dimtih value is false, the dimension text box is aligned with the dimension line or leader line.
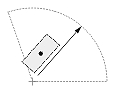
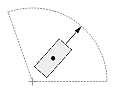
| Dimension type | Dimtih = true | Dimtih = false | ||
| Dimtad = 1, Dimtad = 2 | Dimtad = 0 | Dimtad = 1, Dimtad = 2 | Dimtad = 0 | |
| Linear dimension | 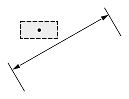 |
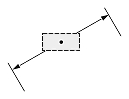 |
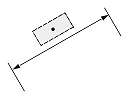 |
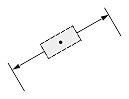 |
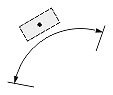
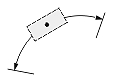
| Angular or arc-length dimension | 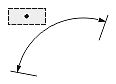 |
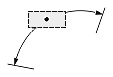 |
 |
 |
| Radial or diametric dimension | 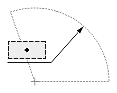 |
 |
 |
 |
| Radial large dimension | 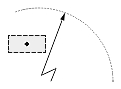 |
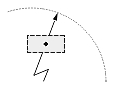 |
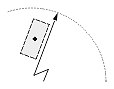 |
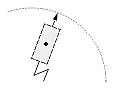 |
The initial value is true.
To get the Dimtih value, use the dimtih() method, which returns Dimtih as a bool value.
For example:
odPrintConsoleString(L"\nDimension text is %s", ((pDimension->dimtih()) ? L"horizontal" : L"aligned with dimension line"));
To set a new Dimtih value, use the setDimtih() method, which requires one bool value as a new Dimtih value.
For example:
pDimension->setDimtih(false);
Dimtoh
The Dimtoh value indicates how the dimension text box is aligned outside the extension lines or definition entity.
If the Dimtoh value is true, the dimension text box is horizontally aligned when it is placed outside the extension lines or definition entity.
If the Dimtoh value is false, the dimension text box is aligned along the dimension line or leader line.
| Dimension type | Dimtoh = true | Dimtoh = false | ||
| Dimtad = 1, Dimtad = 2 | Dimtad = 0 | Dimtad = 1, Dimtad = 2 | Dimtad = 0 | |
| Linear dimension | 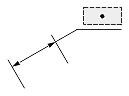 |
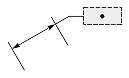 |
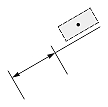 |
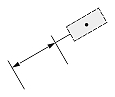 |
| Angular or arc-length dimension | 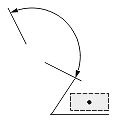 |
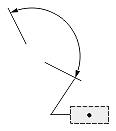 |
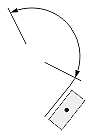 |
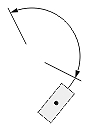 |
| Radial or diametric dimension | 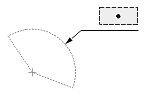 |
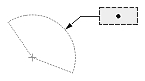 |
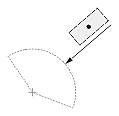 |
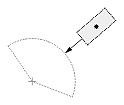 |
| Radial large dimension | 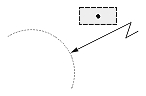 |
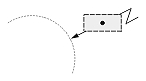 |
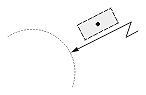 |
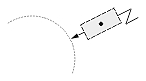 |
The initial value is true.
Note: The Dimtoh value is not available for ordinate dimension entities. The Dimtoh value is not applicable when the TextRotation value is non-zero.
To get the Dimtoh value, use the dimtoh() method, which returns Dimtoh as a bool value.
For example:
odPrintConsoleString(L"\nDimension text is %s outside the extension lines", ((pDimension->dimtoh()) ? L"horizontal" : L"aligned with dimension line"));
To set a new Dimtoh value, use the setDimtoh() method, which requires one bool value as a new Dimtoh value.
For example:
pDimension->setDimtoh(false);
Dimjust
The Dimjust value controls the horizontal justification for the dimension text box (relative to the extension lines). The horizontal justification is an integer value and can be one of the following:
- 0 — The text is centered within the extension lines.
- 1 — The text is by the first extension line.
- 2 — The text is by the second extension line.
- 3 — The text is above the dimension line, parallel to the first extension line.
- 4 — The text is above the dimension line, parallel to the second extension line.
| Dimension type | Dimtad | Dimjust = 0 | Dimjust = 1 | Dimjust = 2 | Dimjust = 3 | Dimjust = 4 |
| Linear dimension | 0 | 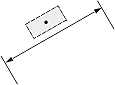 |
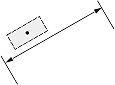 |
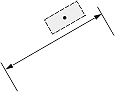 |
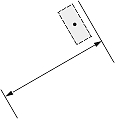
 |
 |
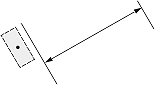
| 1, 2 | 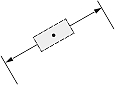 |
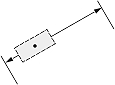 |
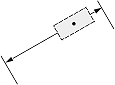 |
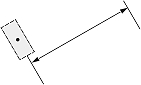 |
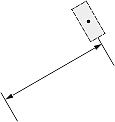 |
|
| Angular or arc-length dimension | 0 | 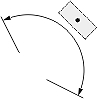 |
 |
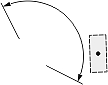 |
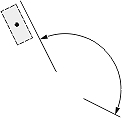 |
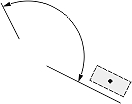 |
| 1, 2 | 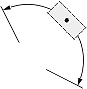 |
 |
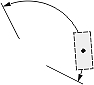 |
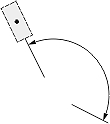 |
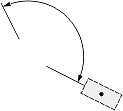 |
The default value is 0.
Note: The Dimjust value is not available for ordinate, diametric, radial, and radial large dimension entities.
To get the Dimjust value use the dimjust() method, which returns the Dimjust value as OdUInt16 value.
For example:
odPrintConsoleString(L"\nDimjust value = %d", pDimension->dimjust());
Dimtix
The Dimtix value indicates the placement of a dimension text box between the extension lines of a dimension entity.
If the value is true, the dimension text box is required to be placed between extension lines.
If the value is false, the dimension text box is placed between extension lines only if there is sufficient space.
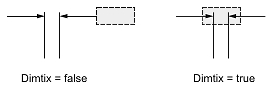
The initial value is false.
To get the Dimtix value, use the dimtix() method, which returns Dimtix as a bool value.
For example:
odPrintConsoleString(L"\nDimension text is placed inside extension lines %s", ((pDimension->dimtoh()) ? L"." : L"if there is room."));
To set a new Dimtix value, use the setDimtix() method, which requires one bool value as a new Dimtix value.
For example:
pDimension->setDimjust(true);
See Also
Working with Common Dimension Entity
Working with General Dimension Methods
Working with Dimension Fit and Movement
Working with Dimension Tolerances
Working with Primary Unit Measurements