The Xline object uses the base point and direction vector properties to define the geometry to be drawn. In examples, the pXLine variable stores the pointer to the Xline object.
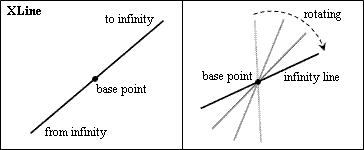
Base Point
The Base Point property defines the base point of the infinite line in three-dimensional coordinates. The base point is the point through which the infinite line passes in the specified direction. Rotating and moving the infinite line are performed relative to the base point. The base point has the coordinates (0,0,0) by default.
To get the base point, use the basePoint() method which does not have arguments and returns the three-dimensional point as an instance of the OdGePoint3d type. For example:
OdGePoint3d point = pXLine->basePoint();
odPrintConsoleString(L"\nBase point = (%g,%g,%g)", point.x, point.y, point.z);
To set the base point, use the setBasePoint() method which requires the three-dimensional point as an argument of the OdGePoint3d type and does not return a value. For example:
OdGePoint3d base(4, 1, 5);
pXLine->setBasePoint(base);
Direction
The property defines the direction of the infinite line in three-dimensional coordinates. The direction is automatically converted to the unit vector which defines the direction from the base point. The direction vector has the coordinates (0,0,1) by default.
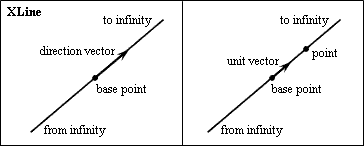
To get the direction, use the unitDir() method which does not have arguments and returns the three-dimensional vector as an instance of the OdGeVector3d type. For example:
OdGeVector3d vector = pXLine->unitDir();
odPrintConsoleString(L"\nDirection = (%g,%g,%g)", vector.x, vector.y, vector.z);
To set the direction, use the setUnitDir() method which requires the three-dimensional vector as an argument of the OdGeVector3d type and does not return a value. For example:
OdGeVector3d direct(0.207, 0.415, 0.207);
pXLine->setUnitDir(direct);
The method automatically converts the specified coordinates to the unit vector. For example:
pXLine->setUnitDir( OdGeVector3d(4.5, 5.2, 6.8) );
OdGeVector3d result = pXLine->unitDir();
odPrintConsoleString(L"\n(%g, %g, %g)", result.x, result.y, result.z);
// (0.465304, 0.537685, 0.703126)