A registered application is an object that defines an external application which uses data attached to objects of a database. The database stores the attached data together with it own objects, but doesn't use them. External applications use the attached data, named extended data (or XData).
Extended data is divided into data sets. Each data set is associated with the external application that uses this data. Any database object can attach a few data sets for various external applications. Each registered application is aware of how to use its corresponding data set within the extended data. To associate extended data with an application, the application must be registered in the database. Names of all registered applications are stored in a special predefined table of the database object. When an application attaches a data set to an object, the database checks the table of the registered applications. If the application is registered, the database saves the data set in its own container and associates data with the application. If an application is not registered, the database generates an exception. Several applications can attach their own data to the same object.
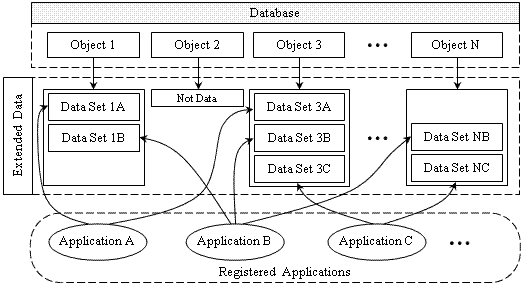
To refer to a registered application, database objects use the name or Object ID. The database associates an ID with each registered application and requires a unique name for each external application in order to identify it. Group codes of a data set use the application name to identify the registered application to which it belongs.