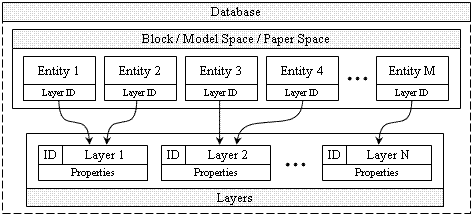
A layer is an object that defines a group of geometric objects (entities) separated by features that can be manipulated as a single unit. Layers separate all entities of a drawing in a functional, logical, or physical way and unite them in groups for the application of similar operations. Such an approach allows for structuring geometric information, manipulating groups of geometry, representing selective properties, ordering parts of a drawing. Using layers also reduces engineering tasks, improves the understanding of the drawing information, and increases work productivity.
A layer is similar to tracing paper used with drawing boards. An engineer draws various fragments of a part on different tracing paper, and then combines the fragments in a general assembly to obtain the final drawing. For each step, or layer, an engineer can solve a restricted set of tasks for each fragment with less complexity than working with the entire drawing. Specific tasks can also be separated and assigned to multiple engineers, each with their own tracing paper, or layer. Additionally, engineers can use one fragment in different drawings, and a single piece of tracing paper can contain a standardized solution or design that could be applied to different productions.
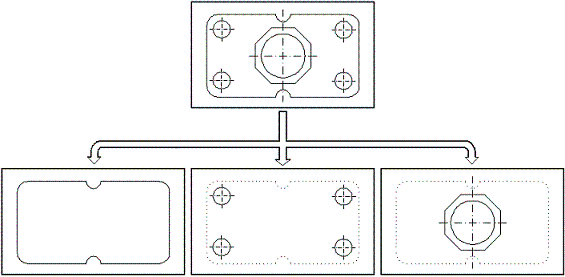
For example, detail of a drawing can be separated on layers according to technology processes, that is, the order of operations to be performed:
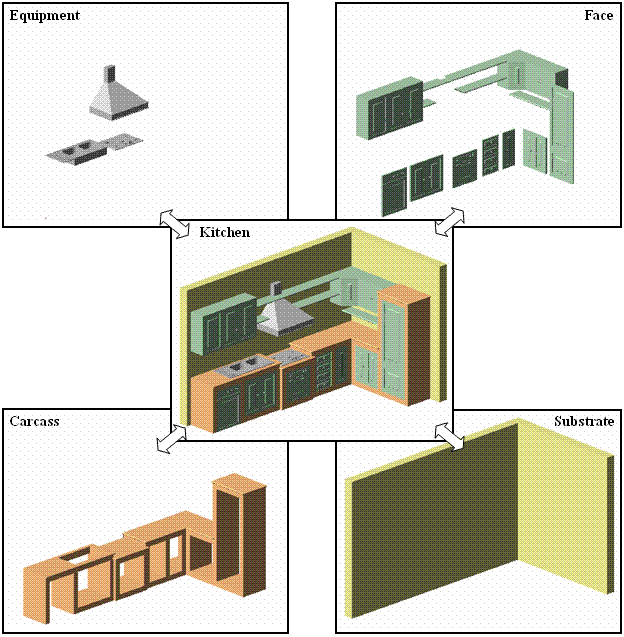
3D entities also can be separated on layers. For example, a kitchen can be separated logically by substrate (wall), shell (base), face (decoration), and equipment (built-in):
A layer can control the following features of entities assigned to the layer:
- Show or hide — Makes entities on a layer visible or invisible.
- Lock or unlock — Makes entities on a layer available or unavailable.
- Freeze or thaw — Includes or exclude entities on a layer from processing.
- Printable or unprintable — Permits or forbids printing of entities on a layer.
- Modify properties — Selects the linetype, lineweight, material, color, transparency of entities on a layer.
A layer is applied only for geometric objects (any entity). To refer to a layer, entities use the layer's Object ID which they store in their own data. Several entities can refer to the same layer. The database associates an ID with each layer and requires a unique name for each layer in order to identify it.