The OdDbMPolygonNode class is used for representing the
tree of nodes for multi-polygons, where one node is one loop. The tree represents
multi-polygon nesting loops. Loops with counterclockwise direction must be placed on even (or zero) levels of the tree. Loops with
clockwise direction that represent holes must be placed on odd levels.
Below is an example of creating a multi-polygon with six nested loops.
OdDbBlockTableRecordPtr pModelSpace = pDb->getModelSpaceId().safeOpenObject(OdDb::kForWrite);
OdDbMPolygonPtr pMPolygon = OdDbMPolygon::createObject();
pMPolygon->setDatabaseDefaults(pDb);
pMPolygon->setPattern(OdDbHatch::kPreDefined, L"SOLID");
pModelSpace->appendOdDbEntity(pMPolygon);
OdGeDoubleArray bugles;
bugles.resize(4, 0);
OdGePoint2dArray vertexArr;
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(0, 0));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(10, 0));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(10, 10));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(0, 10));
pMPolygon->appendMPolygonLoop(vertexArr, bugles); // append loop#0 – counterclockwise
vertexArr.clear();
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(12, 0));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(22, 0));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(22, 10));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(12, 10));
pMPolygon->appendMPolygonLoop(vertexArr, bugles); // append loop#1 – counterclockwise
vertexArr.clear();
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(2, 2));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(2, 8));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(4, 8));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(4, 2));
pMPolygon->appendMPolygonLoop(vertexArr, bugles); // append loop#2 – clockwise
vertexArr.clear();
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(6, 2));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(6, 5));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(9, 5));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(9, 2));
pMPolygon->appendMPolygonLoop(vertexArr, bugles); // append loop#3 – clockwise
vertexArr.clear();
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(14, 2));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(14, 8));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(20, 8));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(20, 2));
pMPolygon->appendMPolygonLoop(vertexArr, bugles); // append loop#4 – clockwise
vertexArr.clear();
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(16, 4));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(18, 4));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(18, 6));
vertexArr.append(OdGePoint2d(16, 6));
pMPolygon->appendMPolygonLoop(vertexArr, bugles); // append loop#5 – counterclockwiseVisualization of the created multi-polygon is shown in the following figure.
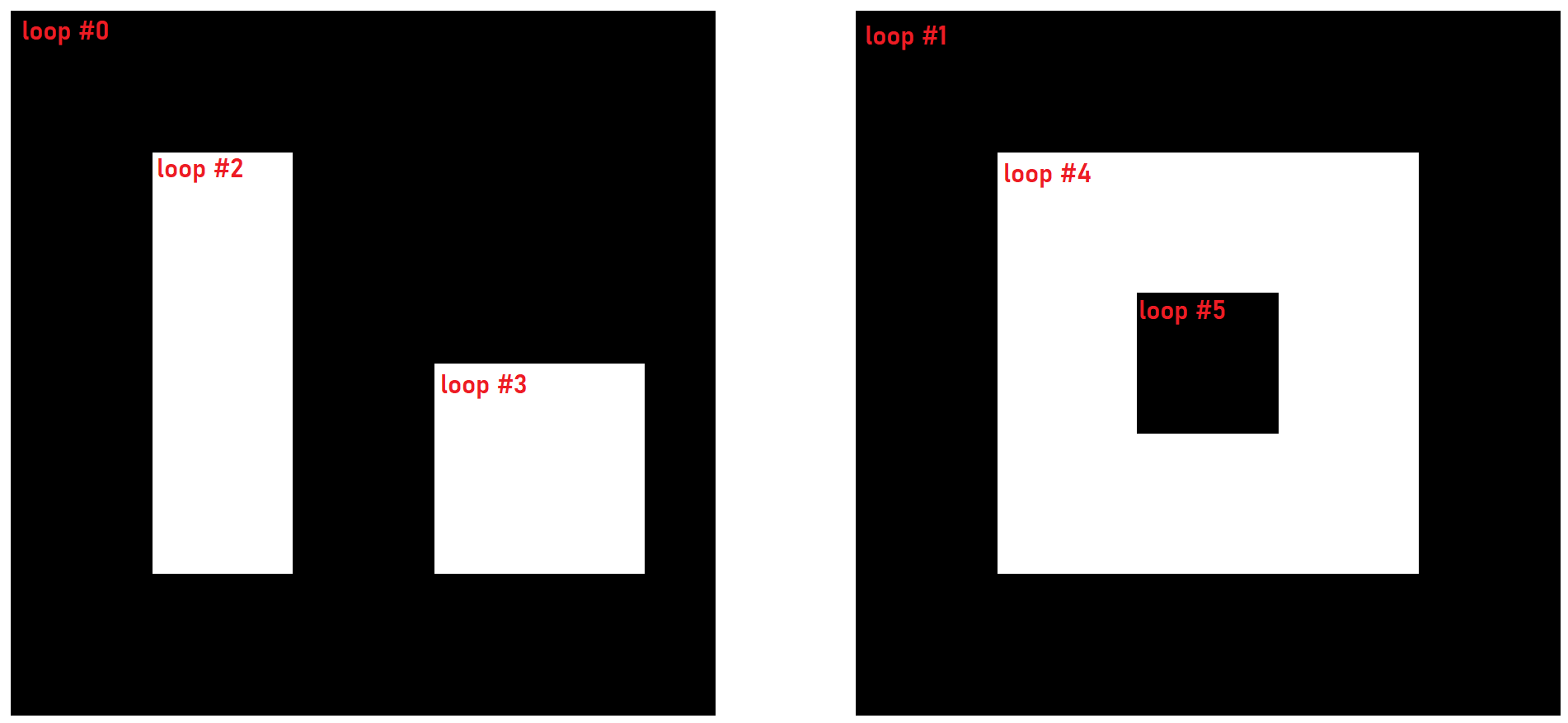
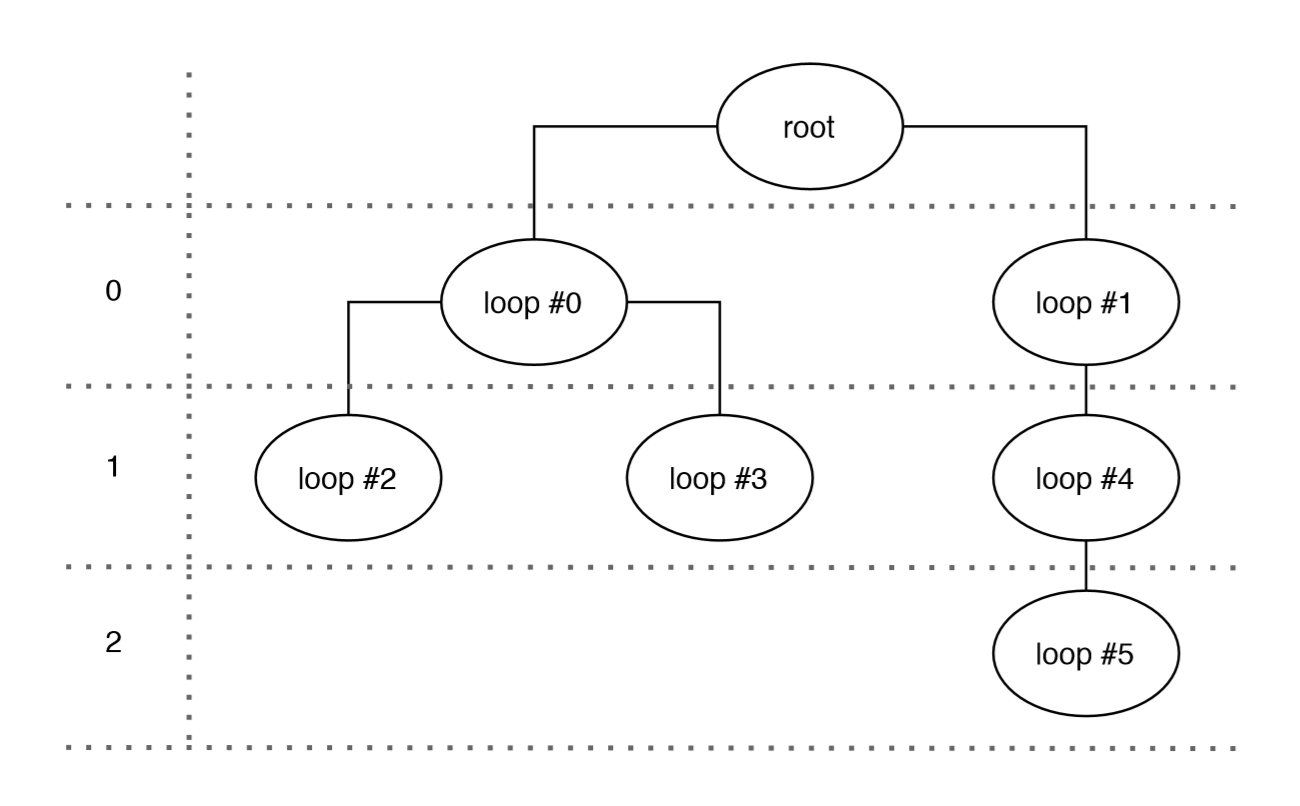
The next figure illustrates an example of the tree.
See Also
Examples of Working with Multi-Polygons
Copyright © 2002 – 2021. Open Design Alliance. All rights reserved.
|